For all we will accomplish together in 2019
and for all you have done to lead the Web to its full potential in 2018,
thank you!
The W3C wishes you a happy holiday season.
by Coralie Mercier via W3C News
For all we will accomplish together in 2019
and for all you have done to lead the Web to its full potential in 2018,
thank you!
The W3C wishes you a happy holiday season.
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group has published Accessible Name and Description Computation 1.1 (Accname) as a W3C Recommendation. Accname describes how user agents determine the names and descriptions of accessible objects from web content languages. The name is a simple label for the object, and the description provides additional information. These are both standard features of accessibility APIs, which allow assistive technologies to identify these objects and present their names or descriptions to users. Documenting the algorithm through which names and descriptions are to be determined promotes interoperable exposure of these properties among different accessibility APIs and helps to ensure that this information appears in a manner consistent with author intent. Separate accessibility API mapping (AAM) specifications define the actual way these features are exposed to accessibility APIs; Accname just describes how the name and description are computed using a variety of content features that may be present at the same time. Read about the Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Dataset Exchange Working Group has published two First Public Working Drafts today:
The CSS Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of CSS Fragmentation Module Level 4. This module describes the fragmentation model that partitions a flow into pages, columns, or regions. It builds on the Page model module and introduces and defines the fragmentation model. It adds functionality for pagination, breaking variable fragment size and orientation, widows and orphans.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, etc.
The Accessible Platform Architectures Working Group and Accessibility Guidelines Working Group have published a First Public Working Draft of Making Content Usable for People with Cognitive and Learning Disabilities and an updated Working Draft of Cognitive Accessibility Roadmap and Gap Analysis, developed by the Cognitive and Learning Disabilities Accessibility (Coga) Task Force. The Making Content Usable for People with Cognitive and Learning Disabilities gives advice on how to make Web content and Web applications usable for people with learning and cognitive disabilities. It was previously an appendix to Cognitive Accessibility Roadmap and Gap Analysis. More information is available in the WAI announcement email. Read about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
Comments are welcome through 14 January 2019.
The Pointer Events Working Group invites implementations of Pointer Events 2 Candidate Recommendation. The features in this specification extend or modify those found in Pointer Events, a W3C Recommendation that describes events and related interfaces for handling hardware agnostic pointer input from devices including a mouse, pen, touchscreen, etc. For compatibility with existing mouse based content, this specification also describes a mapping to fire Mouse Events for other pointer device types.
The Web Real-Time Communications Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of WebRTC Next Version Use Cases. This document describes a set of use cases motivating the development of WebRTC Next Version (WebRTC-NV), as well as the requirements derived from those use cases.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of two updated Candidate Recommendations:
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
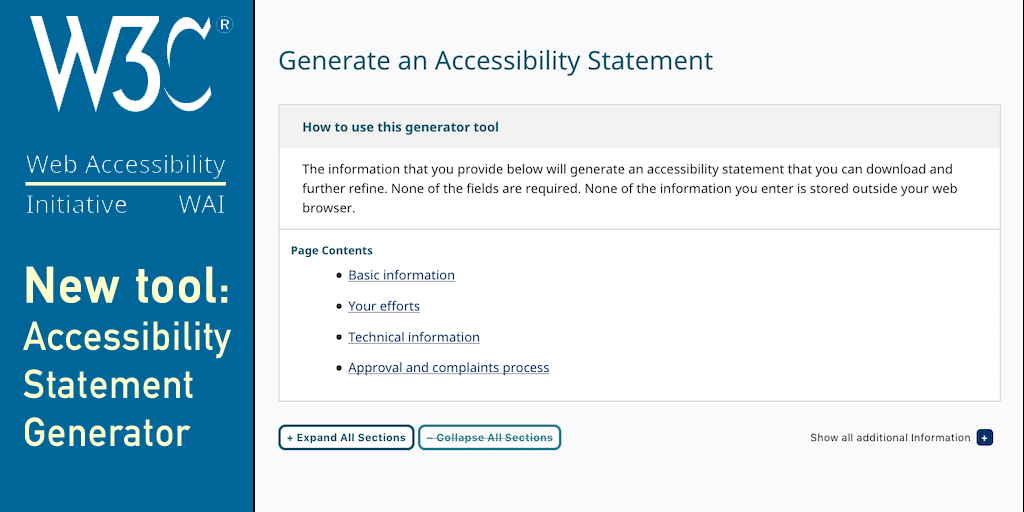 The WAI Education and Outreach Working Group (EOWG) has published Developing an Accessibility Statement.
The WAI Education and Outreach Working Group (EOWG) has published Developing an Accessibility Statement.
The resource helps you create an accessibility statement for your website, mobile app, or other digital content. It includes guidance, examples, and a free generator tool. The tool helps you collect and enter relevant information to create an accessibility statement for your particular content and situation. See more information in How to Create Accessibility Statements blog post.
Learn more about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Spatial Data on the Web Interest Group has published a First Public Working Draft of Extensions to the Semantic Sensor Network Ontology. This specification describes some extensions to the Semantic Sensor Network Ontology, published as a W3C Recommendation in 2017, to enable linking to the ultimate feature-of-interest for an observation, act of sampling, or actuation, and homogeneous collections of observations, in which one or more of the properties may be shared by all members of the collection.
The CSS Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of CSS Shadow Parts. This specification defines the ‘::part()’ pseudo-element on shadow hosts, allowing shadow hosts to selectively expose chosen elements from their shadow tree to the outside page for styling purposes.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
 The WAI Education and Outreach Working Group (EOWG) has published The Business Case for Digital Accessibility. It describes that accessibility can drive innovation, enhance your brand, extend market reach, and minimize legal risk. It includes direct and indirect benefits of accessibility and the risks of not addressing accessibility adequately. It provides case studies and examples that demonstrate how continued investment in accessibility is good for your organization. Learn more about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The WAI Education and Outreach Working Group (EOWG) has published The Business Case for Digital Accessibility. It describes that accessibility can drive innovation, enhance your brand, extend market reach, and minimize legal risk. It includes direct and indirect benefits of accessibility and the risks of not addressing accessibility adequately. It provides case studies and examples that demonstrate how continued investment in accessibility is good for your organization. Learn more about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Timed Text Working Group has published the following specifications as W3C Recommendations:
The Timed Text Markup Language is a content type that represents timed text media for the purpose of interchange among authoring systems. TTML Profiles are intended to be used across subtitle and caption delivery applications worldwide, thereby simplifying interoperability, consistent rendering and conversion to other subtitling and captioning formats.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of two updated Candidate Recommendations:
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, etc.
The Distributed Tracing Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of Trace Context. A distributed application is an application that consists of multiple components, also known as micro-services, that are deployed and operated separately. The Trace Context specification defines properties intended for event correlation between micro-services to allow various tracing and diagnostics monitoring products to operate together.
The CSS Working Group has published Selectors Level 3 as a W3C Recommendation. Selectors are patterns that match against elements in a tree, and as such form one of several technologies that can be used to select nodes in an HTML or XML document. Selectors have been optimized for use with HTML and XML, and are designed to be usable in performance-critical code.
The Accessible Platform Architectures Working Group has published two First Public Working Drafts today:
Read more about the Accessible Platform Architectures Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group has published a Proposed Recommendation of Accessible Name and Description Computation 1.1. This document describes how user agents determine the names and descriptions of accessible objects from web content languages. This information is in turn exposed through accessibility APIs so that assistive technologies can identify these objects and present their names or descriptions to users. Documenting the algorithm through which names and descriptions are to be determined promotes interoperable exposure of these properties among different accessibility APIs and helps to ensure that this information appears in a manner consistent with author intent. Read about the Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
Comments are welcome through 16 November 2018.
The Pointer Events Working Group has published a Proposed Recommendation of Pointer Events Level 2. The features in this specification extend or modify those found in Pointer Events, a W3C Recommendation that describes events and related interfaces for handling hardware agnostic pointer input from devices including a mouse, pen, touchscreen, etc. For compatibility with existing mouse based content, this specification also describes a mapping to fire Mouse Events for other pointer device types.
Comments are welcome through 13 November 2018.
W3C announced today a Workshop on Web Standardization for Graph Data, 4-6 March 2019, in Berlin, Germany. The event is hosted by Neo4J.
This workshop brings together people with an interest in the future of standards relating to graph data, and its ever growing importance in relation to the Internet of Things, smart enterprises, smart cities, etc., open markets of services, and synergies with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML).
The scope includes:
Harmonising different perspectives on database management systems:
Managing the silos, big data, AI and machine learning:
Scalability, security, trust, APIs and vocabulary development:
We aim to share experiences, use case studies, new directions and insights on what’s needed for the next generation of Web data standards.
For more information on the workshop, please see details and submission instructions, and further background information. Expression of Interest and position statements are due by 15 December 2018.
The Timmed Text Working Group published the following specifications as W3C Proposed Recommendations:
The Timed Text Markup Language is a content type that represents timed text media for the purpose of interchange among authoring systems. TTML Profiles are intended to be used across subtitle and caption delivery applications worldwide, thereby simplifying interoperability, consistent rendering and conversion to other subtitling and captioning formats.
Comments are welcome through 1 November 2018.
The W3C SVG Working Group has published an updated Candidate Recommendation of Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 2. TThis specification defines the features and syntax for Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) Version 2. SVG is a language based on XML for describing two-dimensional vector and mixed vector/raster graphics. SVG content is stylable, scalable to different display resolutions, and can be viewed stand-alone, mixed with HTML content, or embedded using XML namespaces within other XML languages. SVG also supports dynamic changes; script can be used to create interactive documents, and animations can be performed using declarative animation features or by using script.
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group has published WAI-ARIA Graphics Module 1.0 (Graphics-ARIA) and Graphics Accessibility API Mappings 1.0 (Graphics-AAM) as W3C Recommendations. Graphics-ARIA defines core roles specific to web graphics which allow an author to express the logical structure of the graphic to assistive technologies in order improve accessibility of graphics. Graphics-AAM defines how user agents map the WAI-ARIA Graphics Module markup to platform accessibility APIs. Assistive technologies could then enable semantic navigation and adapt styling and interactive features, to provide an optimal experience for the audience. Read about the Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
W3C announced today a W3C Workshop on Strong Authentication and Identity, December 10-11 2018, in Redmond, WA, USA. The event is hosted by Microsoft.
This workshop will look to provide an existing standards landscape, roadmap and potential future work for how strong identity and strong authentication should work on the web. A successful workshop will be how to align recent W3C specifications (WebAuthn, Verifiable Claims, Web Payments) and work that is ongoing in the W3C Credentials Community Group (DID, DIDAuth) along with IETF and ISO, as well as other existing community standards such as Open ID Connect, Oauth, SAML, etc.
The scope includes:
For more information on the workshop, please see details and submission instructions. Expression of Interest and position statements are due by 29 October 2018.
The Web Real-Time Communications Working Group invites implementations of two Candidate Recommendations:
The Web Performance Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of Device Memory. This document defines a HTTP Client Hint header to surface device capability for memory i.e. device RAM, in order to enable web apps to customize content depending on device memory constraints.
The CSS Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of CSS Scrollbars Module Level 1. CSS Scrollbars standardizes the ability to color scrollbars introduced in 2000 by Windows IE 5.5. This is useful when building web applications which use color schemes very different from the appearance of default platform scrollbars.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
 The CSS Working Group has published CSS Fonts Module Level 3 as a W3C Recommendation. This CSS Module describes how to specify fonts used in CSS, including Web Fonts downloaded on demand. It also describes how to access advanced typographic features in fonts, and how to control font loading. This specification is implemented in all modern browsers.
The CSS Working Group has published CSS Fonts Module Level 3 as a W3C Recommendation. This CSS Module describes how to specify fonts used in CSS, including Web Fonts downloaded on demand. It also describes how to access advanced typographic features in fonts, and how to control font loading. This specification is implemented in all modern browsers.
 The Audio Working Group invites implementations of Web Audio API Candidate Recommendation. Web Audio is a high-level Web API for processing and synthesizing audio in web applications. The primary paradigm is of an audio routing graph, where a number of AudioNode objects are connected together to define the overall audio rendering. The actual processing will primarily take place in the underlying implementation, but using AudioWorklet, direct script processing and synthesis from JavaScript or Web Assembly is also supported.
The Audio Working Group invites implementations of Web Audio API Candidate Recommendation. Web Audio is a high-level Web API for processing and synthesizing audio in web applications. The primary paradigm is of an audio routing graph, where a number of AudioNode objects are connected together to define the overall audio rendering. The actual processing will primarily take place in the underlying implementation, but using AudioWorklet, direct script processing and synthesis from JavaScript or Web Assembly is also supported.
 Today the World Wide Web Consortium released the Authorized Italian Translation of Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, Linee guida per l’accessibilità dei contenuti Web (WCAG) 2.1, contributed by International Web Association (IWA). This translation of WCAG 2.1 coincides with the adoption of the EU Web Accessibility Directive and the related European Standard EN 301 549, which refers to WCAG 2.1. You may read W3C Blog post to learn more about the Adoption of WCAG 2.1 in Europe. Roberto Scano from IWA, who coordinated the translation, published a blog post in Italian.
Today the World Wide Web Consortium released the Authorized Italian Translation of Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, Linee guida per l’accessibilità dei contenuti Web (WCAG) 2.1, contributed by International Web Association (IWA). This translation of WCAG 2.1 coincides with the adoption of the EU Web Accessibility Directive and the related European Standard EN 301 549, which refers to WCAG 2.1. You may read W3C Blog post to learn more about the Adoption of WCAG 2.1 in Europe. Roberto Scano from IWA, who coordinated the translation, published a blog post in Italian.
The Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) encourages the development of W3C Authorized Translations of WCAG 2.1 in all languages. Read about the Policy for W3C Authorized Translations.
The CSS Working Group has published a Proposed Recommendation of Selectors Level 3. Selectors are patterns that match against elements in a tree, and as such form one of several technologies that can be used to select nodes in an XML document. Selectors have been optimized for use with HTML and XML, and are designed to be usable in performance-critical code. This document describes the selectors that already exist in CSS1 [CSS1] and CSS2 [CSS21], and further introduces new selectors for CSS3 and other languages that may need them.
Comments are welcome through 12 October 2018.
The W3C JSON-LD Working Group has published three First Public Working Drafts today.
The JSON-LD 1.1 Syntax document defines a JSON-based format to serialize Linked Data. The syntax is designed to easily integrate into deployed systems that already use JSON, and provides a smooth upgrade path from JSON to JSON-LD. It is primarily intended to be a way to use Linked Data in Web-based programming environments, to build interoperable Web services, and to store Linked Data in JSON-based storage engines. The 1.1 version of this specification will extend the existing JSON-LD 1.0 Recommendation, published in 2014.
The JSON-LD 1.1 Processing Algorithms and API document defines a set of algorithms for programmatic transformations of JSON-LD documents. Restructuring data according to the defined transformations often dramatically simplifies its usage. Furthermore, this document proposes an Application Programming Interface (API) for developers implementing the specified algorithms. The 1.1 version of this specification will extend the existing JSON-LD Processing Algorithms and API Recommendation, published in 2014.
The JSON-LD 1.1 Framing document defines an approach that allows developers to query by example and force a specific tree layout to a JSON-LD document.
All three documents are derived from Community Group Reports published by the JSON for Linking Data W3C Community Group.
The Working Group welcomes comments via the GitHub repository issues (see the respective documents’ headers for the reference of the repositories).
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of CSS Display Module Level 3 Candidate Recommendation. This module describes how the CSS formatting box tree is generated from the document element tree and defines the ‘display’ property that controls it.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of two updated Candidate Recommendations of CSS Cascading and Inheritance Level 3 and CSS Cascading and Inheritance Level 4. The CSS module defined in these documents describes how to collate style rules and assign values to all properties on all elements. By way of cascading and inheritance, values are propagated for all properties on all elements. New in the Level 4 are the ‘revert’ keyword and <supports-condition> for the ‘@import’ rule.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
The Devices and Sensors Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of Geolocation Sensor. This specification defines the GeolocationSensor interface for obtaining geolocation of the hosting device.
The CSS Working Group has published a Proposed Recommendation of CSS Fonts Module Level 3. This CSS3 module describes how font properties are specified and how font resources are loaded dynamically. The contents of this specification are a consolidation of content previously divided into CSS3 Fonts and CSS3 Web Fonts modules. The description of font load events was moved into the CSS Font Loading module.
Comments are welcome through 11 September 2018.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of two updated Candidate Recommendations of CSS Scroll Snap Module Level 1 and CSS Values and Units Module Level 3, and has just published CSS Values and Units Module Level 4 as a First Public Working Draft.
The CSS Scroll Snap Module contains features to control panning and scrolling behavior with “snap positions”. The CSS module, defined in the CSS Values and Units Module Level 3 and Level 4, describes the common values and units that CSS properties accept and the syntax used for describing them in CSS property definitions. See changes in Level 3 and Level 4.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
The Timed Text Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of Timed Text Markup Language 2 (TTML2). This document specifies the Timed Text Markup Language (TTML), Version 2, also known as TTML2, in terms of a vocabulary and semantics thereof.
The Timed Text Markup Language is a content type that represents timed text media for the purpose of interchange among authoring systems. Timed text is textual information that is intrinsically or extrinsically associated with timing information.
It is intended to be used for the purpose of transcoding or exchanging timed text information among legacy distribution content formats presently in use for subtitling and captioning functions.
In addition to being used for interchange among legacy distribution content formats, TTML Content may be used directly as a distribution format, for example, providing a standard content format to reference from a <track> element in an [HTML 5.2] document, or a <text> or <textstream> media element in a [SMIL 3.0] document.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of a Candidate Recommendation of CSS Painting API Level 1, an API for allowing web developers to define a custom CSS with javascript, which will respond to style and size changes. See EXPLAINER.
The Timed Text Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of Timed Text Markup Language 1 (TTML1) (Third Edition). This document specifies Timed Text Markup Language (TTML), Version 1, also known as TTML1, in terms of a vocabulary and semantics thereof.
The Timed Text Markup Language is a content type that represents timed text media for the purpose of interchange among authoring systems. Timed text is textual information that is intrinsically or extrinsically associated with timing information.
It is intended to be used for the purpose of transcoding or exchanging timed text information among legacy distribution content formats presently in use for subtitling and captioning functions.
In addition to being used for interchange among legacy distribution content formats, TTML Content may be used directly as a distribution format, for example, providing a standard content format to reference from a element in an HTML5 document, or a or media element in a [SMIL 2.1] document.

The contents of the roadmap have been updated to follow the evolution of the Web platform since April 2018. See the Change history for details. Most of these updates focused on mechanisms that allow mobile web applications to tweak performance settings and gain finer-grained control over the browser’s default behavior. In particular, new exploratory work and technologies in progress mentioned in the Performance and Tuning page include:
contain property to indicate that an element’s subtree is independent of the rest of the page,overscroll-behavior property to control the behavior of a scroll container when its scrollport reaches the boundary of its scroll box,The roadmap did not mention WebDriver, recently published as a W3C Recommendation, a key technology for mobile web developers as it enables automated testing across browsers and devices. This was an oversight, fixed in this new version.
The implementation info rendered in tables now also embeds information from the MDN Browser Compatibility Data project. A new “partial” badge also indicates that an implementation may be incomplete, either because it is, or because implementation data is not complete enough to assess support of the entire specification.
Sponsored by Beihang University, this project is part of a set of roadmaps under development in a GitHub repository to document existing standards, highlight ongoing standardization efforts, point out topics under incubation, and discuss technical gaps that may need to be addressed in the future. New versions will be published on a quarterly basis, or as needed depending on progress of key technologies of the Web platform. We encourage the community to review them and raise comments, or suggest new ones, in the repository’s issue tracker.
The SVG Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 2. This specification defines the features and syntax for Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) Version 2. SVG is a language based on XML for describing two-dimensional vector and mixed vector/raster graphics. SVG content is stylable, scalable to different display resolutions, and can be viewed stand-alone, mixed with HTML content, or embedded using XML namespaces within other XML languages. SVG also supports dynamic changes; script can be used to create interactive documents, and animations can be performed using declarative animation features or by using script. This version of SVG builds upon SVG 1.1 Second Edition by improving the usability and precision of the language. The Changes appendix lists all of the changes that have been made since SVG 1.1 Second Edition.
The Web Authentication Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of Web Authentication: An API for accessing Public Key Credentials Level 1. This specification defines an API enabling the creation and use of strong, attested, scoped, public key-based credentials by web applications, for the purpose of strongly authenticating users. Conceptually, one or more public key credentials, each scoped to a given WebAuthn Relying Party, are created and stored on an authenticator by the user agent in conjunction with the web application. The user agent mediates access to public key credentials in order to preserve user privacy. Authenticators are responsible for ensuring that no operation is performed without user consent. Authenticators provide cryptographic proof of their properties to Relying Parties via attestation. This specification also describes the functional model for WebAuthn conformant authenticators, including their signature and attestation functionality.
 On 25 July the ACM has announced W3C’s Judy Brewer as the recipient of the 2018 SIGACCESS Award for Outstanding Contributions to Computing and Accessibility.
On 25 July the ACM has announced W3C’s Judy Brewer as the recipient of the 2018 SIGACCESS Award for Outstanding Contributions to Computing and Accessibility.
The SIGACCESS Award for Outstanding Contributions to Computing and Accessibility recognizes individuals who have made significant and lasting contributions to the development of computing technologies that improve the accessibility of media and services to people with disabilities. This award recognizes members of the community for long-term accomplishments or those who have made a notable impact through a significant innovation.
Judy Brewer is Director of the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), and a Principal Research Scientist at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Lab. For the past 21 years, under Judy’s leadership, WAI has developed key accessibility standards, prominent amongst which are the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), the Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG), User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG), and Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA).
As part of the award, Judy has been invited to present a keynote talk at the ASSETS Conference on October 22nd. Read more about about the SIGACCESS Award, about WCAG and WAI.
The Timed Text Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of TTML Profiles for Internet Media Subtitles and Captions 1.1. This specification defines two profiles of [ttml2-20180628]: a text-only profile and an image-only profile. These profiles are intended to be used across subtitle and caption delivery applications worldwide, thereby simplifying interoperability, consistent rendering and conversion to other subtitling and captioning formats. This specification improves on [ttml-imsc1.0.1] by supporting contemporary practices, while retaining compatibility with [ttml-imsc1.0.1] documents. Relative to [ttml-imsc1.0.1], any addition or deprecation of features are summarized at Appendix L. Summary of substantive changes (non-normative).
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group has published an updated Working Group Note of WAI-ARIA Authoring Practices 1.1. WAI-ARIA Authoring Practices 1.1 was previously published as a Working Group Note in December 2017, to accompany the WAI-ARIA 1.1 Recommendation. Since then, the group has added an additional design pattern and examples, and improved the quality of many of the other design patterns and examples, to improve the support for WAI-ARIA 1.1. Separately, as recently announced, WAI-ARIA Authoring Practices 1.2 is under development, which includes the improvements in this document plus additional features specific to WAI-ARIA 1.2. Each version of WAI-ARIA Authoring Practices is specific to the corresponding version of WAI-ARIA. Read about the Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) Working Group has published three First Public Working Drafts:
These document are part of the WAI-ARIA suite described in the WAI-ARIA Overview.
W3C published today the report of the W3C Workshop on Web5G: Aligning evolutions of network and Web technologies, which was held on 10-11 May 2018, in London.
The report contains a summary of each session with links to the presentation slides. More detailed meeting minutes are also available[1][2].
Network Operators, vendors, application developers, content provider and standard makers participated in this event which was designed to explore how the Open Web Platform could help drive the adoption of 5G innovations from the applications layer to the network level.
During the two days, participants reviewed opportunities that new emerging innovations and capabilities at the application layers can bring to the 5G network. The workshop concluded with the proposed creation of a task force of participants to explore how the 5G and Web communities might work in a productive and cohesive manner.
In particular, there was wide agreement on the benefit of developing compelling business and technical reasons and objectives to incentivize and drive a close collaboration among the W3C, 5G standard organizations (e.g. 3GPP), browser vendors, developers, equipment vendors and network operators. The goal is to create an environment conducive to the development and deployment of technologies that are supported by all the stakeholders in the ecosystem.
We thank our host, GSMA, and the Program Committee for making this event possible.
 W3C announced today a W3C Workshop on Permissions and User Consent, September 18-19, 2018, in San Diego, California, USA. The event is hosted by Qualcomm.
W3C announced today a W3C Workshop on Permissions and User Consent, September 18-19, 2018, in San Diego, California, USA. The event is hosted by Qualcomm.
The primary goal of the workshop is to bring together security and privacy experts, UI/UX researchers, browser vendors, mobile OS developers, API authors, Web publishers and users to address the privacy, security and usability challenges presented by a complex and overlapping variety of permissions and consent systems available for hardware sensors, device capabilities and applications on the Web.
The scope includes:
For more information on the workshop, please see the workshop details and submission instructions. Expression of Interest and position statements are due by August 17, 2018.
The Web Payments Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of Payment Request API. This specification standardizes an API to allow merchants (i.e. web sites selling physical or digital goods) to utilize one or more payment methods with minimal integration. User agents (e.g., browsers) facilitate the payment flow between merchant and user.
The Web Performance Working Group invites implementations of User Timing Level 2 Candidate Recommendation. This specification defines an interface to help web developers measure the performance of their applications by giving them access to high precision timestamps.
![]() The World Wide Web Consortium today launched the Internationalization Initiative to expand core work in further internationalizing the Web. “”Supporting the W3C Internationalization Initiative with funding or expertise is a vital way that our Web community creates the future of the global Web,” said Jeff Jaffe, W3C CEO. W3C thanks Alibaba, Apple, Advanced Publishing Lab (Keio University), Monotype, and The Paciello Group who have stepped up as Founding Sponsors. Read about W3C Internationalization and its Sponsorship Program and the press release and testimonials.
The World Wide Web Consortium today launched the Internationalization Initiative to expand core work in further internationalizing the Web. “”Supporting the W3C Internationalization Initiative with funding or expertise is a vital way that our Web community creates the future of the global Web,” said Jeff Jaffe, W3C CEO. W3C thanks Alibaba, Apple, Advanced Publishing Lab (Keio University), Monotype, and The Paciello Group who have stepped up as Founding Sponsors. Read about W3C Internationalization and its Sponsorship Program and the press release and testimonials.
A wide review Working Draft of Accessibility Conformance Testing (ACT) Rules Format was published today by the Accessibility Guidelines Working Group (AG WG). This draft addresses all comments received on the previous drafts. Most importantly, “Composed Rules” was introduced, in addition to “Atomic Rules”, to replace “Rule Groups”. This draft is accompanied by sample ACT Rules that implement this rules format. Read about the the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Accessible Platform Architectures Working Group has published a Working Draft of a revision to Inaccessibility of CAPTCHA. Since the last publication, the abilities of robots to defeat CAPTCHAs has increased, and new technologies to authenticate human users have come available. This update brings the document up to date with these new realities. For more information, see the blog post Updated and extensively revised “Inaccessibility of CAPTCHA” Published. Read about the Accessible Platform Architectures Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
The Web Real-Time Communications Working Group invites implementations of Identifiers for WebRTC’s Statistics API Candidate Recommendation. This document defines a set of WebIDL objects that allow access to the statistical information about a RTCPeerConnection. These objects are returned from the getStats API that is specified in [WEBRTC].
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of CSS Text Decoration Module Level 3. This module contains the features of CSS relating to text decoration, such as underlines, text shadows, and emphasis marks.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
The Web Real-Time Communications Working Group has published two First Public Working Drafts:
The Timed Text Working Group invites implementations of an updated Timed Text Markup Language 2 (TTML2) Candidate Recommendation. This document specifies the Timed Text Markup Language (TTML), Version 2, also known as TTML2, in terms of a vocabulary and semantics thereof.
The Timed Text Markup Language is a content type that represents timed text media for the purpose of interchange among authoring systems. Timed text is textual information that is intrinsically or extrinsically associated with timing information.
 W3C announced today a W3C Workshop on Digital Publication Layout and Presentation (from Manga to Magazines), September 18-19 2018, in Tokyo, Japan. The event is hosted by the Advanced Publishing Laboratory, at the historic Mita Campus of Keio University.
W3C announced today a W3C Workshop on Digital Publication Layout and Presentation (from Manga to Magazines), September 18-19 2018, in Tokyo, Japan. The event is hosted by the Advanced Publishing Laboratory, at the historic Mita Campus of Keio University.
The primary goal of the workshop is to bring together experts to evaluate the current status and explore future directions of visually-rich long-form digital publications based on Web Technologies (particularly CSS, the formatting language of the Web), encompassing both fixed and dynamic layouts.
Expected topics of discussion include:
For more information on the workshop, please see the workshop details and submission instructions. Expression of Interest and position statements are due by 20 July 2018.
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications Working Group has published two Proposed Recommendations:
These documents are part of the WAI-ARIA suite described in the WAI-ARIA Overview.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of CSS Fonts Module Level 3. This CSS3 module describes how font properties are specified and how font resources are loaded dynamically. The contents of this specification are a consolidation of content previously divided into CSS3 Fonts and CSS3 Web Fonts modules. The description of font load events was moved into the CSS Font Loading module.
The CSS Working Group has published CSS Basic User Interface Module Level 3 (CSS3 UI) as a W3C Recommendation. This specification describes user interface related properties and values that are proposed for CSS level 3 to style HTML and XML (including XHTML). It includes and extends user interface related features from the properties and values of CSS level 2 revision 1. It uses various properties and values to style basic user interface elements in a document. This specification is implemented in all modern browsers.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
The Web Real-Time Communications Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of WebRTC 1.0: Real-time Communication Between Browsers. The WebRTC 1.0 specification defines JavaScript APIs to enable real-time audio, video and data exchange on the Web. Since the previous publication as Candidate Recommendation, the specification was updated with a number of bug fixes and clarifications in its algorithms. The following new APIs were added as part of these improvements: RTCRtpSender.setStreams(), RTCRtpTransceiver.currentDirection, RTCSctpTransport.maxChannels, RTCPeerConnection.onstatsended, and the RTCStatsEvent interface.
 W3C announced today it was offering Diversity Scholarships. The announcement was made as part of the publication of W3C top-level diversity statistics.
W3C announced today it was offering Diversity Scholarships. The announcement was made as part of the publication of W3C top-level diversity statistics.
The lack of diversity in tech is a longstanding issue. We would like W3C to be a model of supporting diversity. As an international organization we can see the immense value we gain from having expertise from across multiple countries and cultures. Soon 50% of the world will be on the Web. We know we will need to reflect the diversity of the whole of our world as more and more people begin to access, use and continue to create the Web in all its full potential.
During the Spring W3C Advisory Committee Meeting, a panel on diversity focused on progress we have made and how much more is required. W3C has established a modest fund for TPAC Diversity Scholarships, sponsored by W3C Members Samsung Electronics, The Paciello Group, Consensus System and Microsoft.
Applicants must be from a traditionally underrepresented and/or marginalized group in the Web community, including but not limited to: persons identifying as LGBTQ, women, persons of color, and/or persons with disabilities; and be unable to attend without some financial assistance. Please submit or share with friends who qualify and might be interested, by 15 July.
If your organization or yourself wishes to become a sponsor, please e-mail us!
 Today June 19th, 2018, Kazuyuki Ashimura, W3C staff contact for WoT and Media and Entertainment was presented by the President of TTC the award for Information Communication Technology in Shiba, Tokyo, Japan, recognizing contributions and promotion of Web standardization in Japan.
Today June 19th, 2018, Kazuyuki Ashimura, W3C staff contact for WoT and Media and Entertainment was presented by the President of TTC the award for Information Communication Technology in Shiba, Tokyo, Japan, recognizing contributions and promotion of Web standardization in Japan.
A W3C team contact since 2005, Kaz has dedicated standardization work in W3C groups for various technical themes, promoting the viewpoint of “global standardization” and bringing Japan’s efforts to global discussions, championing issues for consideration at W3C, and contributing greatly to standardization deliberations. Read more about recent work at W3C in Media & Entertainment, Web of Things (and more).
The CSS Working Group has published CSS Color Module Level 3 as a W3C Edited Recommendation. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a language for describing the rendering of HTML and XML documents on screen, on paper, in speech, etc. It uses color-related properties and values to color the text, backgrounds, borders, and other parts of elements in a document. This specification describes color values and properties for foreground color and group opacity. These include properties and values from CSS level 2 and new values. This specification incorporates errata raised against the previous W3C Recommendation for CSS Color 3. This specification is fully implemented in all modern browsers.
The Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) Working Group invites implementations of Accessible Name and Description Computation 1.1 Candidate Recommendation. This document describes how user agents determine the names and descriptions of accessible objects from web content languages. This information is in turn exposed through accessibility APIs so that assistive technologies can identify these objects and present their names or descriptions to users. Documenting the algorithm through which names and descriptions are to be determined promotes interoperable exposure of these properties among different accessibility APIs and helps to ensure that this information appears in a manner consistent with author intent.
This document updates and will eventually supersede the accessible name and description guidance in the WAI-ARIA 1.0 User Agent Implementation Guide W3C Recommendation. It is part of the WAI-ARIA suite described in the WAI-ARIA Overview.
W3C released today its W3C Strategic Highlights – May 2018, a comprehensive survey of the essential work W3C conducts to achieve a Web for All, and select recent work in many areas where the Web can solve arising problems for real people.
A strong emphasis in this report is how progress in many areas demonstrates both the vitality of the W3C and the Web community. We see the maturation and further development of an incredible number of new technology coming to the Web.
This report, was prepared for the Spring W3C Advisory Committee Meeting. We invite you to read W3C CEO’s summary of the Advisory Committee Meeting.
The EXI Working Group has published Canonical EXI as a W3C Recommendation. The EXI 1.0 format specifies the syntax of a class of resources called EXI streams. It is possible for EXI streams that are equivalent for the purposes of many applications to differ in physical representation. The Canonical EXI Recommendation specifies a method to get a canonical form, to be used with digital signatures. Even restricted and very limited devices should be able to create or check a canonical EXI stream. This applies to devices that may be able to speak only a given language (according to an XML Schema) or support only a subset of all EXI features.
The Browser Testing and Tools Working Group has published WebDriver as a W3C Recommendation. WebDriver is a powerful technology for enabling automated cross-browser testing of Web applications and more. The WebDriver specification defines a set of interfaces and a wire protocol that are platform-neutral and language-neutral and that allow out-of-process programs to remotely control a browser in a way that emulates the actions of a real person using the browser.
 The Accessibility Guidelines Working Group has published Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 as a W3C Recommendation. WCAG 2.1 provides recommendations for making web content more accessible to a wider range of people with disabilities, including auditory, cognitive, neurological, physical, speech, visual disabilities. The guidelines address accessibility of web content on desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. Following these guidelines also makes your web content more usable to all users in a variety of situations. For more information, see the blog post WCAG 2.1 is a W3C Recommendation and see What’s New in WCAG 2.1. Read about the Accessibility Guidelines Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI). Please see our Press Release.
The Accessibility Guidelines Working Group has published Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 as a W3C Recommendation. WCAG 2.1 provides recommendations for making web content more accessible to a wider range of people with disabilities, including auditory, cognitive, neurological, physical, speech, visual disabilities. The guidelines address accessibility of web content on desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. Following these guidelines also makes your web content more usable to all users in a variety of situations. For more information, see the blog post WCAG 2.1 is a W3C Recommendation and see What’s New in WCAG 2.1. Read about the Accessibility Guidelines Working Group and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI). Please see our Press Release.
W3C published today the final report of the W3C Workshop on Data Privacy Controls and Vocabularies, which was held on 17-18 April 2018, in Vienna (Austria).
The workshop examined the opportunities for privacy vocabularies to be used in conjunction with Linked Data in order to open the path for a new generation of privacy enhancing technologies. Those technologies focus on controlling a compliant data handling. They help with the challenges for privacy and security on the Web of Data and the Web of Things.
The workshop gave a strong message of support for W3C to initiate work on Privacy Vocabularies and Taxonomies and to look further into the idea of guiding data handling with Linked Data annotations. As this is partly still exploratory, the people present encouraged the creation of a Community Group. Since then, the W3C Data Privacy Vocabularies and Controls CG (DPVCG) has been launched. Please, join if you are interested in the topic.
 The W3C Advisory Committee has filled five open seats on the W3C Advisory Board. Beginning 1 July 2018, the nine Advisory Board participants are Michael Champion (Microsoft), Jay (Junichi) Kishigami (NTT), Charles McCathie Nevile (Yandex), Florian Rivoal (W3C Invited Expert), Natasha Rooney (GSMA), Tzviya Siegman (Wiley), David Singer (Apple), Léonie Watson (The Paciello Group), and Judy Zhu (Alibaba). Many thanks to Tantek Çelik (Mozilla) and Chris Wilson (Google), whose terms end this month. Read more about the Advisory Board.
The W3C Advisory Committee has filled five open seats on the W3C Advisory Board. Beginning 1 July 2018, the nine Advisory Board participants are Michael Champion (Microsoft), Jay (Junichi) Kishigami (NTT), Charles McCathie Nevile (Yandex), Florian Rivoal (W3C Invited Expert), Natasha Rooney (GSMA), Tzviya Siegman (Wiley), David Singer (Apple), Léonie Watson (The Paciello Group), and Judy Zhu (Alibaba). Many thanks to Tantek Çelik (Mozilla) and Chris Wilson (Google), whose terms end this month. Read more about the Advisory Board.
Created in March 1998, the Advisory Board provides ongoing guidance to the W3C Team on issues of strategy, management, legal matters, process, and conflict resolution. The Advisory Board also serves the W3C Members by tracking issues raised between Advisory Committee meetings, soliciting Member comments on such issues, and proposing actions to resolve these issues. The Advisory Board manages the evolution of the Process Document. The Advisory Board hears appeals of Member Submission requests that are rejected for reasons unrelated to Web architecture. For several years, the AB has conducted its work in a public wiki.
The elected Members of the Advisory Board participate as individual contributors and not representatives of their organizations. Advisory Board participants use their best judgment to find the best solutions for the Web, not just for any particular network, technology, vendor, or user.
The CSS Working Group invites implementations of an updated Candidate Recommendation of CSS Containment Module Level 1. This CSS module describes the 'contain' property, which indicates that the element’s subtree is independent of the rest of the page. This enables heavy optimizations by user agents when used well.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
TooFab |
14 Songs You Gotta Hear on #NewMusicFriday: Cardi B, Selena Gomez, Christina Aguilera, Rita Ora
TooFab The girl collab of the year (so far) is here. Titled appropriately, Rita Ora's new banger -- "Girls" -- dropped Friday. The song features Cardi B, Bebe Rexha and Charli XCX. We're obsessed. Cardi B Says She and Nicki Minaj Talked About Their 'Issue' at ... |
Paste Magazine |
The 15 Best Videogames of 2018 (So Far)
Paste Magazine The internet thrives on instant nostalgia. 2018 is four months old, which makes it one-third dead, which means we've spent just enough time gallivanting through its days to justify an early stab at a best games of the year list. This is a rough draft ... |
E! Online |
Before Christina Aguilera Releases Her Next Album, Relive Her Most Iconic Music Video Moments!
E! Online Your browser does not currently recognize any of the video formats available. Click here to visit our frequently asked questions about HTML5 video. Share. Include playlist. An error occurred while retrieving sharing information. Please try again later. |
Deseret News |
17 songs for your Mother's Day playlist
Deseret News SALT LAKE CITY — In honor of Mother's Day on Sunday, May 13, here's a list of songs that touch on the value and importance of mothers, including sweet tributes singers have written for their moms and songs filled with a mother's sound advice. Please ... |
Gizmodo |
The Many, Many Voices of Batman, Ranked
Gizmodo Many actors have donned the bat-mantle to provide a voice to Gotham's Dark Knight—the latest example being the delightfully loopy Batman Ninja, out now on Blu-ray and DVD—over decades of film, TV, and games. But who's done it best? Here's our ... |
The Independent |
Scott Hutchison death: The late Frightened Rabbit frontman's 10 best songs
The Independent To many fans in the indie-rock community, Frightened Rabbit's Scott Hutchison was more than just a frontman of their favourite band: he was them. Throughout his 36 years on earth, Hutchison sang about his struggles with mental health, personal pain and ... |
ICYMI: Exclusive 'On the Trail' videos from our Spring Recruiting Tour
Rivals.com (press release) Your browser does not currently recognize any of the video formats available. Click here to visit our frequently asked questions about HTML5 video. Share. Include playlist. An error occurred while retrieving sharing information. Please try again later. |
TooFab |
12 Songs You Gotta Hear on #NewMusicFriday: Cardi B, Selena Gomez, Christina Aguilera, Rita Ora
TooFab The girl collab of the year (so far) is here. Titled appropriately, Rita Ora's new banger -- "Girls" -- dropped Friday. The song features Cardi B, Bebe Rexha and Charli XCX. We're obsessed. Cardi B Says She and Nicki Minaj Talked About Their 'Issue' at ... |
 The redesigned W3C WAI website makes it easier to get information to help you improve web accessibility. The visual design, information architecture, navigation, and overall user experience is all new. Much of the content is revised, and we plan to revise more in the coming months. The redesign makes it easier to skim pages, read content, find specific information, and discover new resources. It’s also easier for the community to be involved in improving resources. Please see W3C WAI Website Redesign Information for:
The redesigned W3C WAI website makes it easier to get information to help you improve web accessibility. The visual design, information architecture, navigation, and overall user experience is all new. Much of the content is revised, and we plan to revise more in the coming months. The redesign makes it easier to skim pages, read content, find specific information, and discover new resources. It’s also easier for the community to be involved in improving resources. Please see W3C WAI Website Redesign Information for: